 |
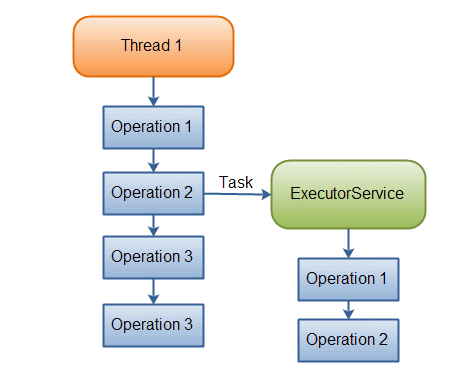
Java 1.5 въведе
java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService интерфейс, който предоставя
ансинхронен механизъм
за изпълнение на нишки. Имплементацията му - класът
ThreadPoolExecutor се реализира чрез банка от нишки
(thread pool), на които се подават задачи (Task) за изпълнение . |
 |
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, |
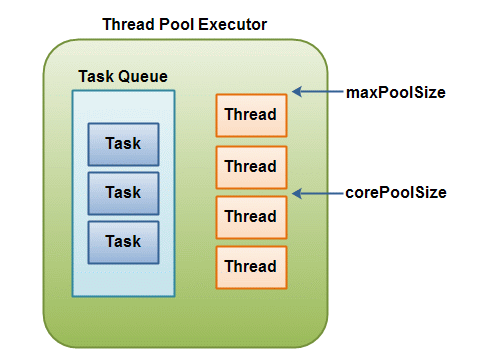
ThreadPoolExecutor автоматично нагласява the pool
size (виж getPoolSize())
съобразно границите поставени от corePoolSize (виж getCorePoolSize()),
maximumPoolSize (виж getMaximumPoolSize())
и размера на опашката от задачи.
При подаване на нова задача от метода execute(java.lang.Runnable),
и нишките в pool-а са по-малко от corePoolSize ,
се създава нова нишка дори и да има чакащи задачи нишки в pool-а.
Ако броя на нишките в pool-а е равен или по-голям
от corePoolSize но по-малък от maximumPoolSize
нова нишка се създава само ако максималният размер на опашката е
запълнен.. Задавайки еднаква стойност на corePoolSize и
maximumPoolSize се задава pool с фиксиран размер на нишките. Чрез
задаването на неограничена стойност на maximumPoolSize например Integer.MAX_VALUE,
и ограничаването на опашката се разрешава на
pool-а да приема неограничен брой нишки. Обикновено core и
maximum pool sizes се задават при конструирането на pool-а,
но могат да бъдат и променяни по време на работа чрез setCorePoolSize(int)
и setMaximumPoolSize(int).
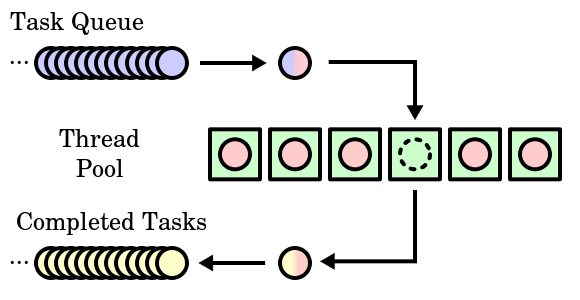 |
броят на нишките - от съществено значение
|
| import
java.util.concurrent.*; public class ThreadPoolTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int nTasks = 20; // number of tasks to be submitted to pool long n = 30; //Fibonacci number int tpSize = 5; // corePoolSize LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable> q; ThreadPoolExecutor tpe = new ThreadPoolExecutor( tpSize, tpSize, 50000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, ( q=new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>( ))); /* public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) */ System.out.println("Initial number of threads:"+tpe.getActiveCount()); Task[] tasks = new Task[nTasks]; for (int i = 0; i < nTasks; i++) { tasks[i] = new Task(n, "Task " + i,tpe); tpe.execute(tasks[i]); System.out.println("submittint task "+i+ " number of active threads "+tpe.getActiveCount()+ " number of task in the queue "+q.size()); } tpe.shutdown( ); } } ---------------------------------------- import java.util.*; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.text.*; public class Task implements Runnable { long n; String id; ThreadPoolExecutor tpe; private long fib(long n) { if (n == 0) return 0L; if (n == 1) return 1L; return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2); } public Task(long n, String id, ThreadPoolExecutor tpe) { this.n = n; this.id = id; this.tpe=tpe; } public void run( ) { Date d = new Date( ); DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss:SSS"); long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis( ); d.setTime(startTime); System.out.println("Starting task " + id + " at " + df.format(d)+ "; active threads:" +tpe.getActiveCount()); System.out.println("\tfibonatchi "+ n+":"+ fib(n)); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis( ); d.setTime(endTime); System.out.println("\tEnding task " + id + " at " + df.format(d) +" after " + (endTime - startTime) + " milliseconds"); } } |
------------------------------ Числата на Фибоначи образуват редица: F(0) = 1 F(1) = 1 F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2) Започва се с 0 и 1, а всеки следващ член на редицата се получава като сума на предходните два. Първите няколко числа на Фибоначи са: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610, 987 |
| public
class Cabine { private int free; Cabine(int free){ this.free = free; } synchronized void takeCabine(){ while(free==0){ System.out.println("there is no free cabine, "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" waiting"); try{ wait(); } catch(InterruptedException e){ System.err.println(e); } } free--; System.out.println("the cabine is taken by "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+", there is "+free+" free cabines"); } synchronized void releaseCabine(){ free++; System.out.println("the cabine is released by "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+", there is "+free+" free cabines"); notifyAll(); } } |
| public
class Basket { private int free; Basket(int free){ this.free = free; } synchronized void takeBasket(){ while(free==0){ System.out.println("there is no free basket, "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" waiting"); try{ wait(); } catch(InterruptedException e){ System.err.println(e); } } free--; System.out.println("the basket is taken by "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+", there is "+free+" free baskets"); } synchronized void releaseBasket(){ free++; System.out.println("the basket is released by "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+", there is "+free+" free baskets"); notifyAll(); } } |
| public
class Client implements Runnable{ String name; static int n=0; Cabine c; Basket b; Client(Cabine c, Basket b){ name = "Client "+ ++n; this.c=c; this.b = b; try { System.out.println(" creating new client:"+name); Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*50)); } catch (InterruptedException e){} } public void run(){ try { System.out.println(this+" going to the swim pool"); Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*50)); } catch (InterruptedException e){} System.out.println(this+" try to take basket"); b.takeBasket(); try { System.out.println(this+" going to the cabine"); Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*50)); } catch (InterruptedException e){} System.out.println(this+" try to take cabine"); c.takeCabine(); try { System.out.println(this+" changing"); Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*600)); } catch (InterruptedException e){} System.out.println(this+" release cabin"); c.releaseCabine(); try { System.out.println(this+" swimimg"); Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*2000)); } catch (InterruptedException e){} System.out.println(this+" try to take cabine"); c.takeCabine(); try { System.out.println(this+" changing"); Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*600)); } catch (InterruptedException e){} System.out.println(this+" release cabin"); c.releaseCabine(); System.out.println(this+" release basket"); b.releaseBasket(); System.out.println(this+" going home"); } public String toString(){ return name; } } |
| import
java.util.concurrent.*; public class SwimPool { public static void main(String[] args) { int coreThr=7; LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable> q; ThreadPoolExecutor tpe = new ThreadPoolExecutor( coreThr, coreThr, 5000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, (q=new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>( ))); Cabine c=new Cabine(2); Basket b = new Basket(3); for(int i = 0; i<15;i++){ tpe.execute(new Client(c,b)); System.out.println("next client,there is "+q.size()+" elements in queue"); try{ Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e){} } tpe.shutdown(); } } |
| public
class Bridge { private int nVh,cnt_cons, max_cons; private boolean closed; Bridge(int max_cons){ nVh = cnt_cons=0; closed = false; this.max_cons=max_cons; } synchronized public int brN(){ return nVh; } synchronized public void takeB(boolean lr ){ while((nVh>0)&& (lr==true)|| (nVh<0) && (lr==false)||closed){ System.out.println("\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" waiting"); try{ wait(); } catch(InterruptedException e){ System.err.println(e); } } if (lr) nVh--; else nVh++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" on the bridge"); cnt_cons++; if(cnt_cons>=max_cons)closed =true; if(closed)System.out.println("The bridge is closed"); } synchronized public void leaveB(boolean lr ){ if (nVh>0) nVh--; else nVh++; System.out.println("\t\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" leave the bridge"); if(nVh==0) { cnt_cons=0; closed = false; System.out.println("The bridge is open"); } notifyAll(); } } |
| public
class Vehicle implements Runnable{ boolean lr; Bridge b; String name; static int num; Vehicle(boolean lr, Bridge b){ this.lr=lr; this.b = b; name = "V "+ ++num + (lr?" left->":" <-right"); } public void run(){ Thread.currentThread().setName(name); b.takeB(lr); try { Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*200)); } catch (InterruptedException e){} b.leaveB(lr); } public String toString() { return name; } } |
| import
java.util.concurrent.*; public class Circ { static Bridge b = new Bridge(3); public static void main(String arg[]){ int coreThr=7; ThreadPoolExecutor tpe = new ThreadPoolExecutor( coreThr, coreThr, 5000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, (new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>( ))); for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){ tpe.execute(new Vehicle(Math.random()>0.5?true:false, b)); try { Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*50)); } catch (InterruptedException ex) {} } tpe.shutdown(); } } |